Antarctica and Greenland Ice Sheet Drainage Basins
For the IMBIE 2024 assessment, participants are requested to use the following definitions of grounded ice area and drainage basin:
- – For the Antarctic Ice Sheet (AIS), please use the basins mapped by Rignot et al. (2016).
- – For the Greenland Ice Sheet (GRIS), please use the drainage basins mapped by Mouginot et al. (2019).
For the IMBIE 2024 assessment, we are aiming at producing reconciled time-series of mass changes for the 18 drainage basins of Antarctica and 7 sectors of Greenland (see details below). The definition of drainage basins is very important to produce regional assessment of mass balance and assess differences between techniques, therefore all participants are requested to post their results using these sets of drainage basins.
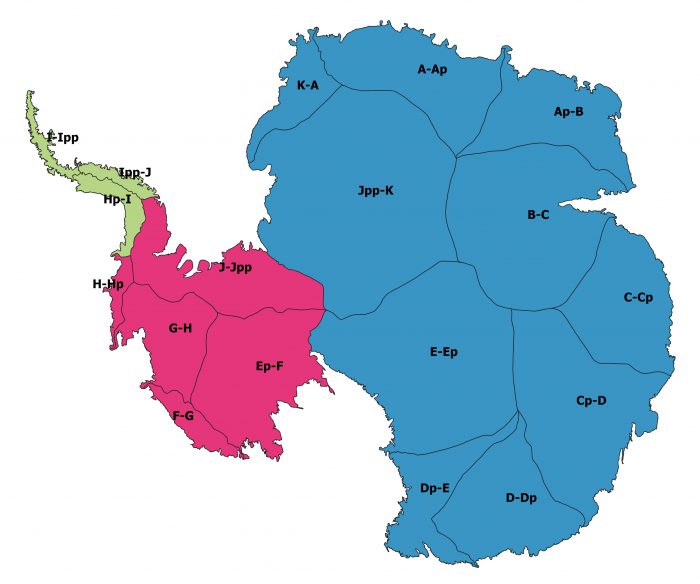
Rignot Basins for AIS
Antarctica is divided into the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, East Antarctic Ice Sheet and Antarctic Peninsula (AP) based on historical definitions plus information from modern-day DEM and ice velocity data. AP is limited by Ronne to the east and George VI to the west. WAIS and EAIS are divided along the Transantarctic range; WAIS drains into Ronne, EAIS drains into Filchner. The basin boundaries are defined with a posting of ~ 150m. Within these three ice sheet regions, subregions A, B, C, Cp, etc. are defined based on historical nomenclature (Giovinetto and Zwally, 2000) plus modern DEM and ice velocity data, and adjusted to match the drainage boundaries of the major ice shelves. Grounding lines, area, ice fronts of all ice shelves are based on (Rignot et al., 2013). The interior basins rely on an ERS/ICESat DEM in the interior and the 2011 velocity mosaic (flow direction) near the coast. The basins are close to an earlier definition (Rignot et al., 2011) where no area is left out, and hence can be used for altimetry, gravity and mass-budget alike. Grounding lines are InSAR 2011 (NSIDC). Surrounding glaciers and ice caps are in one separate shape file. Sub-sub-divisions are not included at this stage.
Rignot Antarctic Drainage Basins
Reference
- Giovinetto, M.B. and H.J. Zwally, 2000. Spatial distribution of net surface accumulation on the Antarctic ice sheet. Annals of Glaciology, 31, 171-178, DOI: 10.3189/172756400781820200
- Rignot, E., J. Mouginot, and B. Scheuchl, 2011. Antarctic Grounding Line Mapping from Differential Satellite Radar Interferometry, Geophysical Research Letters, 38, L10504, DOI: 10.1029/2011GL047109
- Rignot, E., S. Jacobs, J. Mouginot, and B. Scheuchl, 2013. Ice Shelf Melting Around Antarctica. Science, 341(6143): 266-270. DOI: 10.1126/science.1235798
Mouginot Basins for GRIS
Greenland is divided into 7 regions named South West (SW), Central West (CW), North West (NW), North (NO), North East (NE), Central East (CE), and South East (SE) based on ice flow direction and surface slope. These regions are separated based on glacier regime (marine-terminating dominance versus land-terminating) and SMB (dry vs wet) and are of comparable size and ice production. These drainage basin definitions were derived using a composite velocity mosaic from Mouginot et al. (2017) and surface slope from GIMP DEM (Howat et al., 2014). Surrounding glaciers and ice caps are excluded from the basins defined by Mouginot et al. (2019). Sub-division into individual glacier catchments are not required at this stage.
Mouginot Greenland Basins
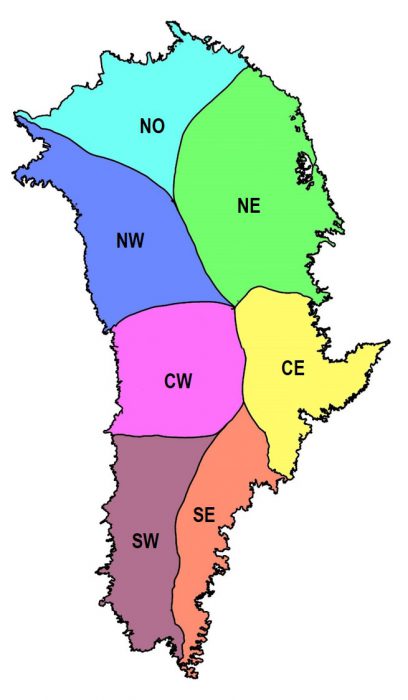
Greenland drainage basin and ice sheet definitions produced by J. Mouginot and E. Rignot.
Reference
- Mouginot J, Rignot E, Scheuchl B, Millan R (2017) Comprehensive annual ice sheet velocity mapping using landsat-8, sentinel-1, and radarsat-2 data. Remote Sensing, 9(4), DOI: 10.3390/rs9040364
- Howat IM, Negrete A, Smith BE (2014) The greenland ice mapping project (gimp) land classification and surface elevation data sets. The Cryosphere, 8(4):1509–1518, DOI: 10.5194/tc-8-1509-2014
- Mouginot J, Rignot E (2019). Glacier catchments/basins for the Greenland Ice Sheet [Dataset]. Dryad. DOI: 10.7280/D1WT11